行业新闻
The Key Role of Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) in Renewable Energy Integration
日期:2025-09-15 浏览次数:13
The intermittency of renewable energy poses challenges for electricity supply. Solar panels only generate power during the day, while wind turbines depend on weather conditions. As power systems increasingly integrate variable renewable energy sources like solar and wind, the demand for flexible and reliable grids that can supply power at any time becomes crucial.
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) can address these supply-demand gaps by providing flexibility to balance supply and demand in real time. When renewable energy generation exceeds demand, batteries store excess electricity for later use, allowing the grid to accommodate higher shares of renewable energy and providing power when the supply from time and weather conditions is uncertain.
Since 2018, energy shifting has become the primary use for power storage, accounting for 67% of the total capacity increase in 2024. This typically involves using BESS to store renewable energy during periods of low market prices or overproduction, then releasing it back into the grid during higher price periods or peak demand times.
Power BESS is divided into two main categories: utility-scale batteries and behind-the-meter batteries. Utility-scale batteries are connected to distribution or transmission networks or generation assets. The storage capacity of these systems typically ranges from several megawatt-hours to hundreds of megawatt-hours, used for grid applications such as frequency regulation and energy shifting.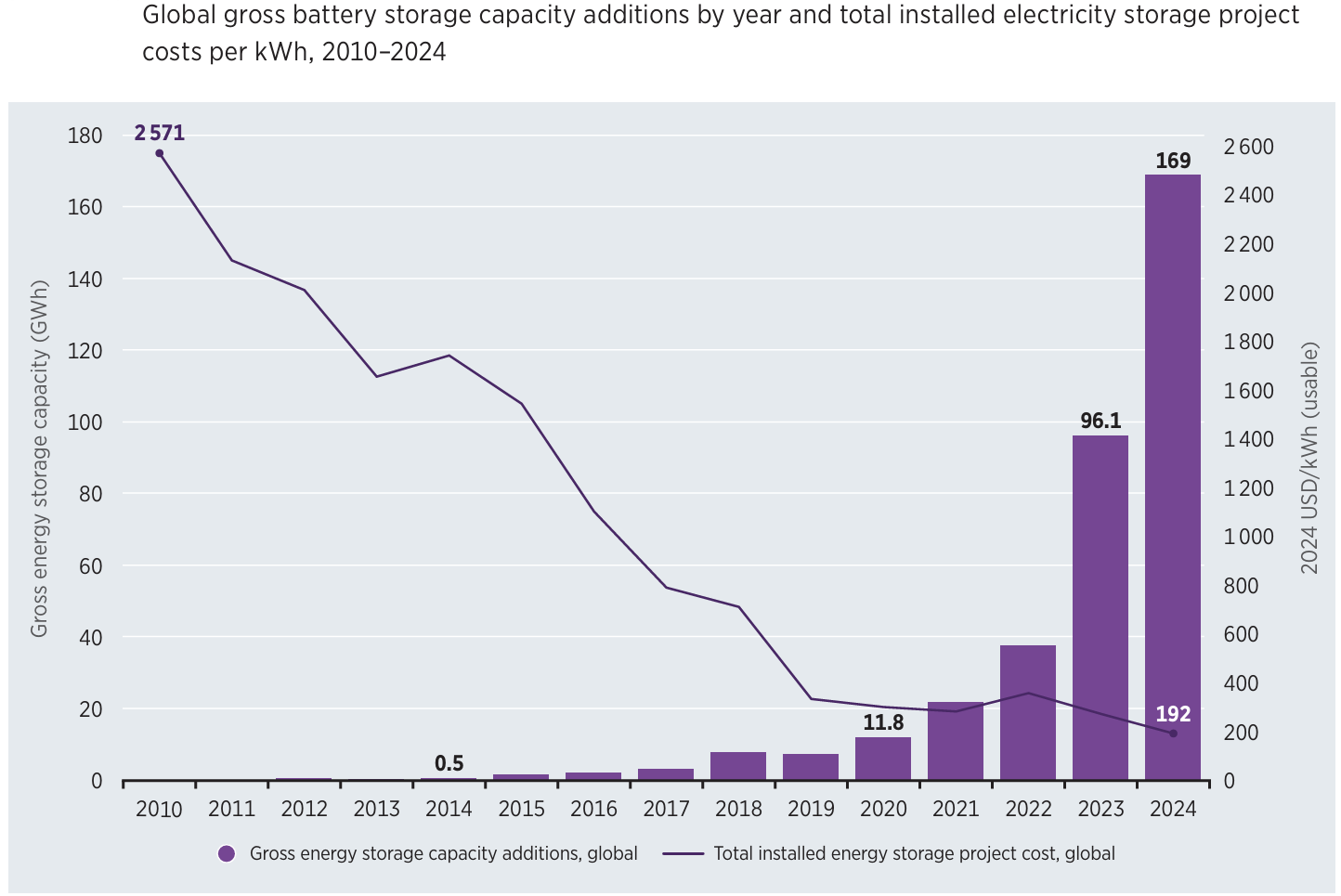
Behind-the-meter systems are connected through the meter and serve commercial, industrial, and residential customers. They are typically installed alongside rooftop solar PV systems and are primarily used for cost savings, demand-side management, and backup power.
The range of battery technologies reflects the different requirements of storage applications. Each battery type has a specific set of characteristics that enable it to meet particular storage needs, whether it is for quick grid response requiring fast power delivery or for long-term storage requiring prolonged discharge periods.
Over the past 15 years, battery storage costs have dropped significantly due to technological advances and increased global manufacturing, leading to economies of scale. From 2010 to 2024, the global cost of fully installed battery storage projects fell by 93%, from $2,571 per kWh to $192 per kWh. Furthermore, compared to 2023, the cost of battery storage for 2-hour systems in 2024 decreased by 38%, and for 4-hour systems, by 32%.
In utility-scale and behind-the-meter applications, lithium-ion batteries have established a market leadership position. Their adoption has been driven by higher efficiency, longer lifespan, and deeper discharge depths compared to other battery technologies. Competition between suppliers across the entire value chain—especially in China, where strong production capacity has already been built—has also driven costs down.
In the lithium-ion sector, a shift towards lithium iron phosphate (LFP) chemistry is underway, especially in utility-scale deployments. LFP's market share has grown from 48% in 2021 to an estimated 85% in 2024, thanks to its lower cost, longer cycle life, and better safety.
Additionally, the costs of battery raw materials such as lithium, nickel, and cobalt have remained relatively low. This trend is partly due to stable or falling prices for battery metals, as new mining and refining capacity comes online and demand expectations soften.
As storage costs decline, the total cost of renewable energy generation and storage solutions is becoming increasingly competitive with traditional power sources. With more supportive policies and market mechanisms being introduced, BESS is expected to become a cornerstone technology for integrating high levels of renewable energy into power systems, making renewable energy more attractive to both producers and consumers.
To further explore this trend and potential policies that could strengthen the business case for battery storage, listen to the latest episode of the IRENA podcast, "All Renewable Energy," featuring Deborah Ayres from the agency's renewable energy cost team.









